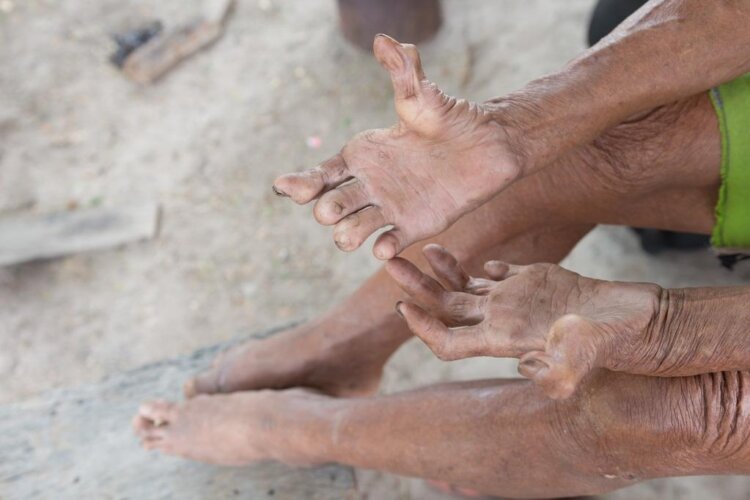
Leprosy in India: Leprosy instances are increasing in different sections of the country. According to an Indian Express report, Mumbai has seen an upsurge in leprosy cases, with 626 cases reported in 2022-23.
Using health department data, Indian Express reported an 87% increase from 2021-22, when it recorded 335 instances. The number of newly identified leprosy cases increased to 626 in 2022-23, the most since 2013-14, when 627 cases were reported.
According to reports, an increase in the proportion of patients in an advanced stage of the disease is causing anxiety among health professionals. According to Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya, India still accounts for more than half (52%) of the world’s new leprosy sufferers.
Meanwhile, leprosy cases have risen in the Southeast United States. As a result, health professionals are concerned that this infectious disease would become prevalent in the region shortly.
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), central Florida is responsible for approximately one-fifth of all cases in the country and 81% of all cases reported in the state.
What is Leprosy?
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines leprosy as a chronic infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae. The condition affects the skin, peripheral nerves, upper respiratory tract mucosa, and the eyes.
The World Health Organization says that leprosy is curable and that early treatment can prevent disability. A person suffering from leprosy is frequently stigmatized and discriminated against.
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) are found in over 120 countries, with over 200 000 new cases recorded each year.
According to 2019 data, Brazil, India, and Indonesia reported over 10,000 new cases, while 13 other countries (Bangladesh, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Mozambique, Myanmar, Nepal, Nigeria, the Philippines, Somalia, , South Sudan, Sri Lanka and the United Republic of Tanzania) each reported 1000–10 000 new cases, WHO revealed.
How leprosy is transmitted?
Leprosy is spread by droplets from the nose and mouth, according to the WHO. The disease must be caught through months of intimate contact with someone who has untreated leprosy, according to the World Health Organization.
It is worth noting that incidental contact with a person who has leprosy, such as shaking hands or embracing, sharing meals or sitting close to each other, does not spread the illness.
When treatment begins, the leprosy sufferer stops transferring the disease.
What are the symptoms of leprosy?
According to CDC, the disease can cause skin symptoms such as:
- Discolored patches of skin, usually flat, that may be numb and look faded (lighter than the skin around)
- Growths (nodules) on the skin
- Thick, stiff or dry skin
- Painless ulcers on the soles of feet
- Painless swelling or lumps on the face or earlobes
- Loss of eyebrows or eyelashes
Symptoms caused by damage to the nerves are:
- Numbness of affected areas of the skin
- Muscle weakness or paralysis (especially in the hands and feet)
- Enlarged nerves (especially those around the elbow and knee and in the sides of the neck)
- Eye problems that may lead to blindness (when facial nerves are affected)
Symptoms caused by the disease in the mucous membranes are:
- A stuffy nose
- Nosebleeds
If left untreated, the signs of advanced leprosy can include:
- Paralysis and crippling of hands and feet
- Shortening of toes and fingers due to reabsorption
- Chronic non-healing ulcers on the bottoms of the feet
- Blindness
- Loss of eyebrows
- Nose disfigurement
Other complications that may sometimes occur are:
- Painful or tender nerves
- Redness and pain around the affected area
- Burning sensation in the skin
How leprosy is treated?
Leprosy is treated with a combination of antibiotics, according to the CDC. Typically, two or three antibiotics are taken concurrently. Treatment often lasts one to two years. The healthy body revealed that the condition can be treated if treatment is done as advised.
Source:FE







 Finance
Finance