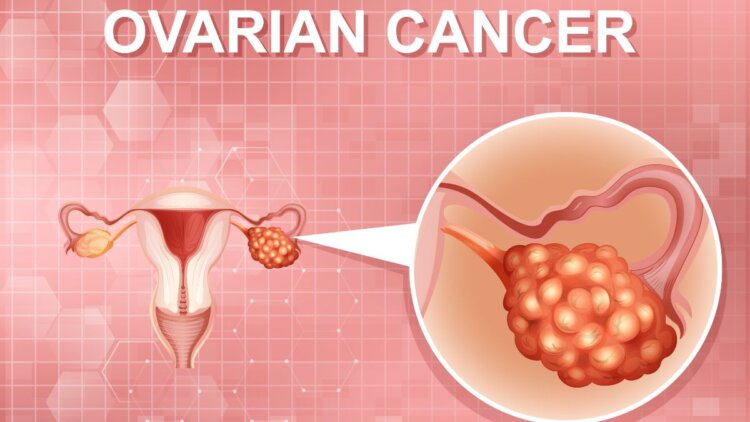
Ovarian cancer is a major health problem among women. It is basically the growth of cells in the ovaries that infiltrate the body and kill healthy body components. There is no single reason for a lump or tumor to develop inside the body, but there are several. It is more common in women after menopause, but that does not diminish the importance of maintaining excellent health in young females. Ovarian cancer symptoms can be overlooked. These have a silent effect on the body and are frequently diagnosed at a later stage. This emphasizes the need of remaining mindful of one’s own body. Because several early symptoms of ovarian cancer may overlap with other prevalent illnesses, it is a silent killer for women. The danger considerations involve an interplay of genetics, environment, and hormones.
OVARIAN CANCER RISK FACTORS
Age: Age is an important factor to consider; ovarian cancer primarily affects women over the age of 50, and the risk increases significantly after menopause.
Genes: Family history is important, especially if there is a history of ovarian, breast, or other cancers. If there are mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, the elevated risk becomes more concerning.
Medical History: Personal medical history is also important, especially if individuals have a family history of breast, colon, or uterine cancer. Women who have not been pregnant or had their first pregnancy after the age of 35 face slightly higher risks.
Menstruation: Early menstruation or late menopause exacerbates this. HRT intricacies must be considered, with long-term estrogen-only HRT potentially raising risk, however combo therapy appears to minimize it.
OVARIAN CANCER EARLY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Dr. Meenu Walia, Senior Director – Medical Oncology, Max Super Speciality Hospital, Patparganj, told that ovarian cancer is commonly referred to as the “silent killer” due to its proclivity for asymptomatic early stages, which complicates identification. However, there are subtle indications that women should be aware of:
- Abdominal Discomfort: The persistence of bloating, pain, or pelvic discomfort can signal an underlying concern.
- Changes in Urination: Heightened urgency, frequent urination, or sustained post-urination fullness may raise suspicion.
- Digestive Issues: Unexplained indigestion, nausea, or shifts in appetite could provide crucial clues.
- Fatigue: Inexplicable fatigue unrelieved by rest might serve as an early indicator.
- Pain During Intercourse: Some women may experience discomfort during sexual activity.
- Change in Menstrual Patterns: Sudden irregularities or shifts in menstrual cycles warrant attention.
- Back Pain: Chronic lower back pain unrelated to known causes could hint at an underlying issue.
It is critical to recognize that these symptoms can be caused by less serious illnesses. However, if these consistently new symptoms do not improve with time, consulting a healthcare professional becomes essential. Early identification and diagnosis play an essential role in improving the prognosis of ovarian cancer.
Source:In








 Finance
Finance