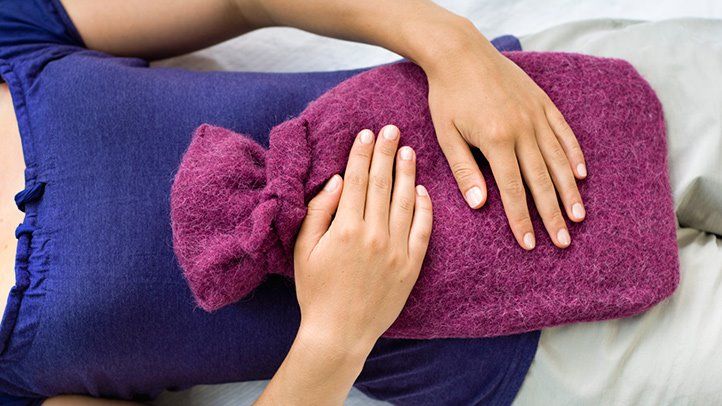
Cramping and pain are pretty frequent during menstruation. Period discomfort affects more than half of menstruators for one to two days during their cycle. These cramps normally occur at the start of your cycle.
Dr. Jagriti Varshney, gynaecologist and obstetrician, explained the source of severe cramps, “During menstruation, the thickened endometrium-the uterine lining sheds away.” This is triggered by hormone-like chemicals known as prostaglandins, which also have a role in uterine contractions, discomfort, and inflammation,” and these symptoms result in monthly cramps.
She went on to say that while a typical degree of discomfort is common and occurs in every menstrual woman, if the severity of the symptoms is greater, it could be due to a high quantity of prostaglandins, which causes certain pathologies such as fibroids, endometriosis or ovarian cyst.
Here are the dos and don’ts when it comes to using pain killers for period pain, as per Dr Varshney
It is typically okay to take pain relievers for cramps, but if the symptoms prevent you from doing your everyday activities, you should see your gynaecologist. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) such as mefenamic acid and ibuprofen, on the other hand, can be used to treat mild to moderate pain. NSAIDs inhibit the formation of prostaglandins, which cause menstrual cramps. However, there is a specific dosage that must be followed. Ibuprofen is best taken in 200 mg doses, while mefenamic acid is best taken in 250 mg doses. Within an eight-hour period, just one to two tablets may be eaten.
Furthermore, because these NSAIDs might induce gastrointestinal difficulties, specialists recommend that they be taken only after a full meal.
If you consume more than the recommended amount, , it can cause several side-effects. Excessive use can lead to increased nausea and vomiting as these symptoms already exist for women suffering from premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
It can also cause constipation, heartburn, high blood pressure and stomach pain. The lesser-known risks associated with excessive usage of NSAIDs are stomach ulcers or bleeding, kidney and heart problems.
The natural remedies that can replace painkillers are:
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid extra bloating
- Eat anti-inflammatory food such as tomatoes, berries, pineapples, ginger, green leafy vegetables, almonds and walnuts
- Dietary supplements such as vitamin D, E and omega-3 fatty acids
- Apply heat on the lower abdominal area
- Exercise releases endorphins in our bodies which leads to muscle relaxation
Source:IE








 Finance
Finance