Taking care of our health is something we should do all our lives. These actions, which range from eating a balanced diet and exercising frequently to getting regular checkups, provide us the power to stay well. The cervix, or bottom section of the uterus attaching to the vagina, is an important part of women’s health. Although many women might not have any issues, the cervix can develop cervical cancer, an avoidable malignancy. Women of all ages can be affected, although those over 30 are more likely to experience it. When detected early, cervical cancer is frequently curable and greatly preventive.
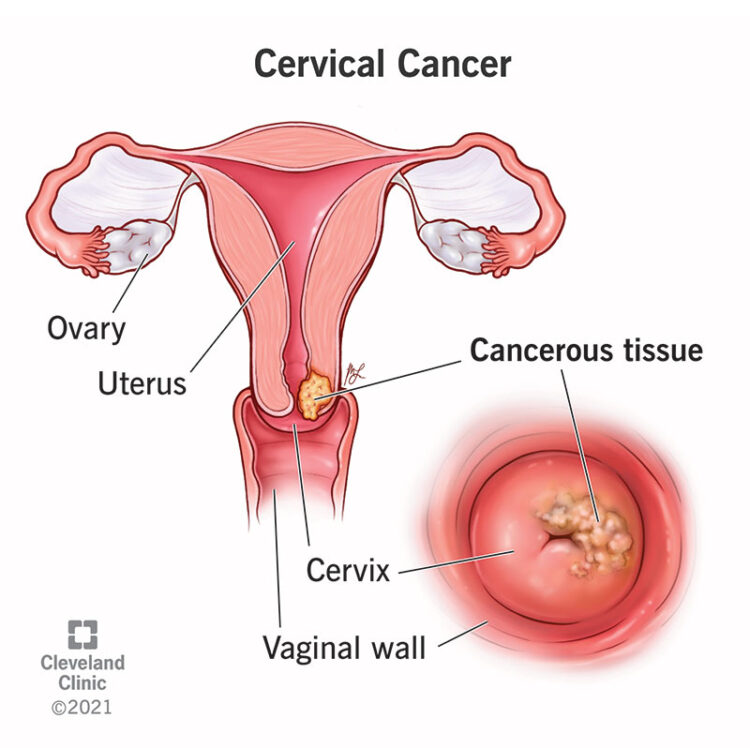
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cervix; while it can affect women of any age, women over 30 are more likely to be affected. The good news is that, with early detection, cervical cancer is largely preventable and often curable. Persistent infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is commonly contracted through sexual intercourse, is the primary cause of cervical cancer. Although the majority of HPV infections go away on their own, certain strains can persist and cause aberrant cervix cell development. If these aberrant cells are not treated, they may eventually turn into cancer.
Early-stage cervical cancer symptoms are rarely seen. Regular screening is essential for early detection because of this. Common screening methods include Pap smears and HPV tests. These tests can identify precancerous changes in the cervix, allowing for treatment before cancer develops. Let’s delve deeper into understanding this cancer, its causes, and the best ways to protect ourselves.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
In the beginning, cervical cancer may not have any symptoms, but as it gets worse, certain signs may show up. These signs include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding post-menopause
- Pelvic pain during sex
- Unusual vaginal discharge
In the beginning, cervical cancer may not have any symptoms, but as it gets worse, certain signs may show up. These signs include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding between periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding post-menopause
- Pelvic pain during sex
- Unusual vaginal discharge
Pain in the lower back or pelvis certain factors can increase your risk of developing cervical cancer, including:
- Smoking
- Weakened immune system due to HIV or other conditions
- Multiple sexual partners
- Early age of first sexual intercourse
- Family history of cervical cancer
Prevention And Treatment
According to Dr. Sangram Keshari Panda, Surgical Oncology, HCG Panda Cancer Hospital, Telengapentha, Cuttack, “The two main strategies for preventing cervical cancer are vaccination and regular screening:”
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection with the strains of HPV most associated with cervical cancer. It is recommended for girls and boys starting at age 9 and can be given up to age 26.
- Screening: Regular Pap smears or HPV tests are crucial for early detection. The recommended frequency of screening may vary depending on your age and risk factors.
He added, “Treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage and extent of the cancer. It may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Early detection significantly improves treatment success rates and often allows for less invasive treatments.”
Early Detection Tips
- Schedule regular Pap smears or HPV tests as recommended by your doctor.
- Be aware of potential symptoms and discuss any unusual changes with your doctor.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by not smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and eating a balanced diet.
- Get vaccinated against HPV.
It’s important to keep in mind that, with a few easy precautions like vaccination and routine screenings, cervical cancer can be mostly avoided. You can greatly lower your chance of getting this cancer by taking proactive care of your health and learning about preventive methods. Frequent screenings also aid in early cancer detection, enabling timely treatment if necessary. By being proactive, you may safeguard yourself against cervical cancer and put your health first.
Source:In








 Finance
Finance