Many people find that changing their diet can assist with osteoarthritis symptoms like pain, stiffness, and swelling. However, because everyone is different and there are numerous varieties of arthritis, what works for one person may not work for another.
However, multiple studies have found associations between arthritis and diet, so it is still important to consider what we consume. The two most important things to consider are:
Losing weight can ease joint strain and lessen the need for painkillers.
Balanced Diet with Vitamins and Minerals Consuming adequate antioxidants, such as vitamins A, C, and E, may assist to avoid future damage to the.Research indicates that getting the correct amount of vitamin C aids in preventing inflammatory arthritis and maintaining healthy joints with osteoarthritis
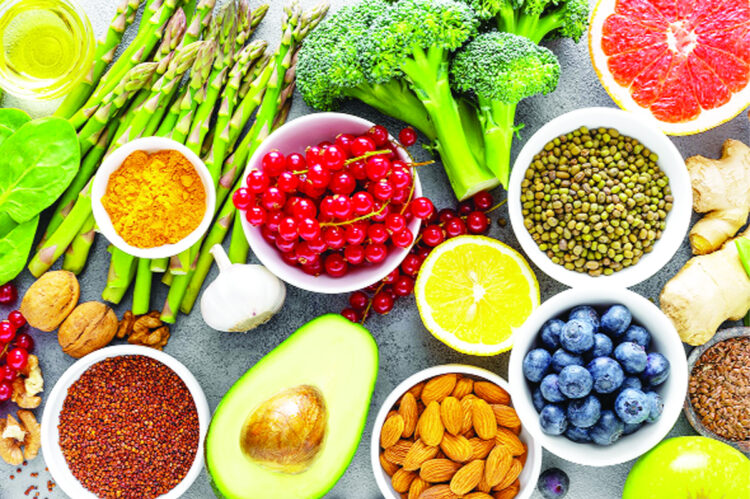
Food can be very powerful in its ability to help, or hurt, our bodies. Few superfoods that are commonly available and are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, but talk to your doctor about whether or not these are right for you.
Superfoods that can help reduce the risk of Arthritis
Fatty fish: Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout contain omega-3 fatty acids, which have powerful anti-inflammatory qualities. Omega-3s aid to inhibit the development of inflammatory proteins like cytokines, which can cause joint inflammation and arthritis symptoms. Regular ingestion of fatty fish can help relieve joint pain and stiffness, particularly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Berries: Berries, such as blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries, are high in antioxidants such anthocyanins and quercetin, which can help reduce inflammation. These antioxidants function by neutralizing free radicals, which can cause oxidative stress and inflammation in the body, potentially contributing to the development of arthritis. Berries are also strong in vitamin C, which helps to preserve collagen in cartilage, which is an important component of healthy joints.
Leafy greens: Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are high in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, which can help reduce inflammation and the risk of arthritis. These greens include high levels of vitamins C, E, and K, which help to protect joint cells from harm. Vitamin K, in particular, helps to maintain strong bones and may lower the chance of developing osteoarthritis.
Nuts: Nuts can help reduce inflammation and the risk of developing arthritis. Walnuts, in example, are high in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an omega-3 fatty acid that can help reduce inflammatory indicators in the body. Nuts contain magnesium, selenium, and vitamin E, all of which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities. Regularly eating a moderate amount of nuts can support overall joint health and reduce inflammation.
Olive oil: Olive oil, particularly extra virgin olive oil, contains oleocanthal, a chemical that has been proven to have anti-inflammatory properties comparable to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen. Oleocanthal suppresses the generation of inflammatory enzymes, reducing joint discomfort and inflammation.
Turmeric: Turmeric is a spice often used in Indian cuisine that includes curcumin, a potent chemical known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant qualities. Curcumin has been found to inhibit inflammatory pathways in the body, which may alleviate arthritic symptoms such as pain and joint stiffness. According to studies, curcumin may be as helpful as other anti-inflammatory medicines in treating arthritis symptoms.
Garlic: Garlic is another superfood that has powerful anti-inflammatory qualities and can help lower the risk of arthritis. Garlic contains diallyl disulfide, a chemical that may help prevent the generation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, lowering joint inflammation. Garlic also contains antioxidants that help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage, which are common in arthritis.
Incorporating these superfoods into your diet can help reduce inflammation, improve joint health, and minimize your chances of developing arthritis.
Disclaimer: This content including advice provides generic information only. It is in no way a substitute for a qualified medical opinion. Always consult a specialist or your own doctor for more information.
Source:NDtv








 Finance
Finance