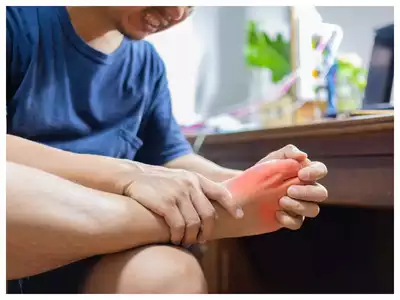
Imagine waking up after a good night’s sleep with a swollen joint, redness, or limited movement. When it happens repeatedly, your body is telling you that something isn’t working properly. Such unusual occurrences may be indicators and symptoms of excessive uric acid or hyperuricemia.
When the body breaks down a chemical called purine, it produces waste called uric acid. Typically, uric acid dissolves in the blood and is excreted by the kidneys. Crystal formation can occur when the kidney fails to effectively drain it out or when uric acid waste is produced in excess. This may cause gout flares. Gout is a kind of arthritis that causes swelling in the joints.
6 Signs of High Uric Acid
- Sudden pain in toe: One may experience sudden pain in the toe. This could be a gout flare up that may happen owing to high levels of uric acid
- Intense joint pain: One of the most characteristic symptoms of high uric acid levels is sudden and intense joint pain, particularly in the big toe. This pain can occur suddenly, often at night, and may be described as sharp or throbbing. The discomfort is typically most severe during the first 12 to 24 hours and can last for several days.
- Tophi: Uric acid crystals may form under the skin. This affects the joint areas and may risk of damaging internal organs too.
- Swelling in joints: Affected joints may become swollen and inflamed due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals. This swelling can make the joint appear red and puffy. In some cases, the skin over the joint may feel warm to the touch, indicating inflammation and irritation.
- Redness: Individuals suffering from high uric acid levels may notice changes in the skin around affected joints. This can include redness, a shiny appearance, or peeling skin. Such changes often accompany swelling and inflammation, indicating ongoing irritation from the crystal deposits.
- Limited leg movement: As the crystals build up in the joints, individuals may experience a decreased range of motion. This limitation can make it difficult to move the affected joint without pain. Over time, this can lead to stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity.
Source: In







 Finance
Finance