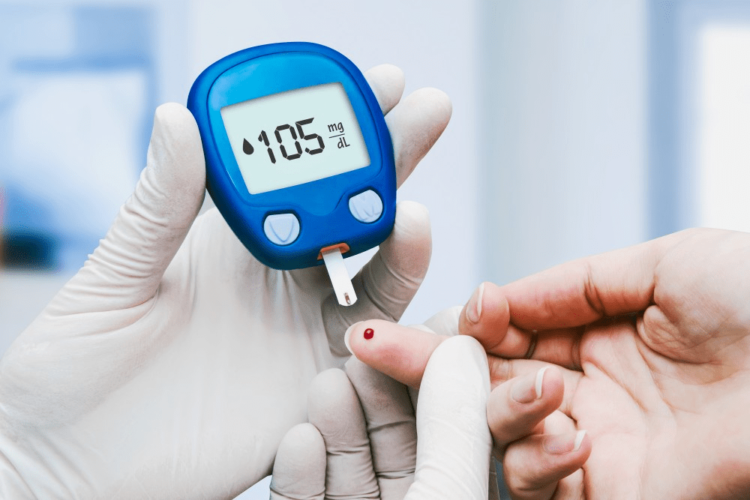
Diabetes not only causes strokes and cardiovascular disease, but it also destroys bones and joints. Hyperglycemia, or high blood glucose levels, is the leading cause of bone weakness, joint pain, and slowed healing, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as osteoarthritis (a degenerative disease of joints characterized by pain, stiffness, and inflammation) and frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis resulting in restriction of movements in the shoulder joint). According to Dr. Aashish Arbat, Orthopedic & Joint Replacement Surgeon at Jehangir Multispeciality Hospitals in Pune, patients with diabetes are more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis and ligament sprains, therefore joint care is an important element of diabetes management.
High blood glucose affects bones and joints
- Weak bones: Diabetes interferes with the balance between bone building and bone breakdown, causing bone density to decrease. This weakens bones and makes them more prone to fractures.
- Joint pain and stiffness: Hyperglycemia causes inflammation of the joints, resulting in pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. Therefore, one will have a hard time performing daily tasks with ease.
- Delayed healing: Inadequate blood flow due to diabetes reduces the rate at which fractures and joint injuries heal.
- Increased risk of osteoarthritis: Diabetics are at a greater risk of developing osteoarthritis, especially in the knees, owing to weight gain, inflammation, and joint damage, which leads to wear and tear.
- Frozen Shoulder: Diabetes also welcomes a condition known as adhesive capsulitis, or frozen shoulder, leading to extreme stiffness and pain in the shoulder joint.
- Ligament Injuries: Elevated glucose levels weaken the ligaments, thus leaving diabetic individuals susceptible to injuries that will require prompt intervention.
Essential advice for diabetic patients:
Choose a calcium- and vitamin-rich diet, including dairy products, green vegetables, nuts, and fish in your meals. Similarly, avoid eating processed foods high in sugar and refined carbs to reduce inflammation. Daily weight-bearing activities such as walking, resistance training, and yoga can help to strengthen bones and increase joint flexibility. Cycling and swimming are also good options for persons who have joint pain. To reduce joint tension, stop smoking and drinking alcohol, and maintain an ideal body weight.
Treatment:
In severe cases, robotic knee replacement may be recommended to the patient. This less invasive operation accurately replaces knee joints, allowing for speedier recovery. It is very beneficial for diabetic people with osteoarthritis. Arthroscopic techniques can repair joint injury with less risk than traditional surgery. Diabetes patients should have their bone and joint issues diagnosed early on. Regular bone scans, joint examinations, and annual check-ups can help discover problems early and prevent immobility.
Source: Intv








 Finance
Finance