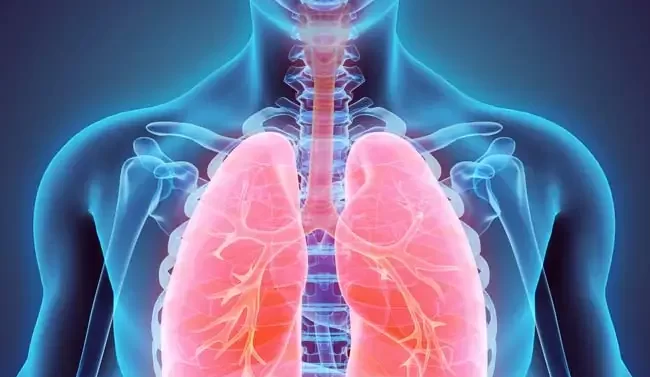
One common environmental hazard that poses serious risks to lung health is air pollution. Nine out of ten people who live in urban areas worldwide are affected by it, making it the ninth most important risk factor for cardiopulmonary mortality.
Air pollution has a variety of harmful effects on the lungs, from aggravating pre-existing conditions to causing entirely new ones.
Chronic respiratory conditions like asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can be brought on by prolonged exposure to air pollution. Particularly dangerous substances include nitrogen oxides, ozone, and particulate matter because they change lung function and cause inflammation.
In extreme cases, exposure to these pollutants can even lead to lung cancer. Children and the elderly are especially vulnerable due to their less efficient or impaired particle clearance mechanisms.
Overall air quality in Delhi continues to be in the ‘Very Poor’ category with the latest AQI being 303.
Dr GC Khilnani, Chairman of the PSRI Institute of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, previously told one digital media that, there has been an exponential rise in patients experiencing acute asthma and COPD attacks.
Even those who were stable for an extended period are now presenting with severe cough, wheezing, breathlessness, and sleepless nights.
Experts advise against self-administering antibiotics, but they also advise against going outside in the early morning when it’s cloudy and there are a lot of pollutants in the air.
Nonetheless, there are a number of preventative steps that can be done to lessen the harm that air pollution causes to lung health.
Observe AQI
It is essential to routinely check the quality of the air in your area. You can plan your outdoor activities more effectively by following AirNow.gov, which provides daily air conditions. Steer clear of busy areas and outdoor exercise on days with poor air quality.
Mask up
When feasible, switch to active transportation instead of driving a car, and select routes that reduce your exposure to nearby air pollution. If you must be outside during a period of heavy pollution, wear masks and limit your physical activity.
Maintain indoor air quality
The quality of the air indoors is equally vital. Make sure your house is properly ventilated and refrain from burning wood or trash. Avoid second- and third-hand smoke as it can combine with indoor pollutants to form compounds that damage the lungs.
Use air purifiers
Despite the lack of solid scientific proof, people with underlying medical conditions may benefit from air purifiers in sealed rooms.
Source:IT








 Finance
Finance