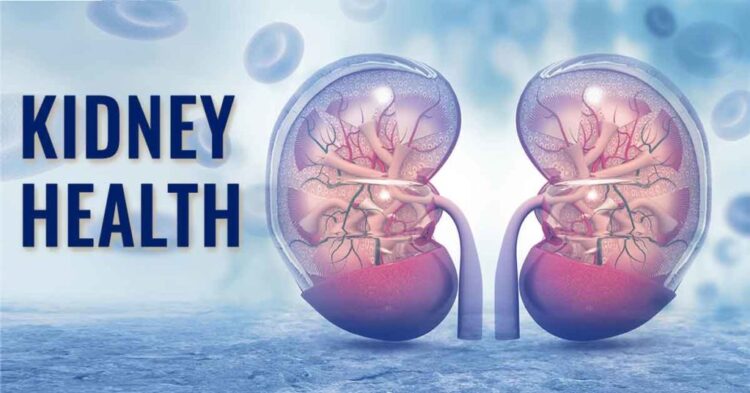
A diet characterised by high sugar intake is a significant factor in compromising kidney health.
The kidneys’ primary job is to create urine and rid your body of waste materials from the blood. Through the release of hormones and regulation of red blood cell synthesis, they also aid in the management of blood pressure.
Eating foods high in sugar on a regular basis might put stress on the kidneys. Consuming a lot of sugar raises blood pressure, which makes the kidneys work harder to filter and eliminate more glucose from the blood.
“Over time, this increased workload can lead to kidney damage, manifesting as proteinuria, CKD (chronic kidney disease), and eventually ESRD (end-stage renal failure), if left uncontrolled. Therefore, maintaining a balanced diet low in sugar is crucial for preserving kidney health, particularly for those with diabetes or predisposed to kidney problems,” said Dr Kamlesh Parikh, Consultant Nephrologist, Kidney Transplant Physician, Bhailal Amin General Hospital, Vadodara.
Dr Soubeer Ghosh, Consultation, Nephrology, PSRI Hospital, New Delhi, added that the kidneys have a handling capacity which gets compromised with a high-sugar diet.
“When the sugar levels go above 180 mg per decilitre, this leads to spillover of sugar in the urine. If the sugar is persistently high, which happens in diabetics, then it destroys the filtration capacity of the kidney gradually,” said Dr Soubeer Ghosh.
Consuming a lot of sugar can aggravate diseases like diabetes and obesity, which increase the risk of kidney damage. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to high blood sugar levels can harm the kidneys’ tiny blood capillaries, which might result in renal failure or injury.
Maintaining kidney health requires eating a diet high in nutrients and low in sugar, especially for people who have diabetes or are prone to renal problems.
Dr Reetesh Sharma, Director & Head, Nephrology & Kidney Transplant Medicine, Asian Hospital, Faridabad, told IndiaToday.In people should monitor their blood pressure, which affects kidney health.
“Uncontrolled blood sugar causes kidney damage. The risk of developing diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is about 25%. The initial stages of DKD lead to an increase in loss of protein in the urine, which is called albuminuria. Over the years, this damages the kidneys,” said Dr Reetesh Sharma.
Dr Ghosh added that if the sugar is persistently high, which happens in diabetics, then it destroys the filtration capacity of the kidney gradually. This leads to kidney injury developing into sodium and water retention.
A 2023 study, published in Frontiers in Nutrition, linked a diet high in sugar and kidney stones.
In a study spanning 11 years and involving 28,303 persons (48 percent of whom were men), kidney stones were 88% more common in those who ate at least 25% of their daily calories from added sugars than in those who limited their consumption to less than 5% of daily calories.
Individuals with diabetes should check for kidney illness and monitor their blood pressure every six months, according to Dr. Kamlesh Parikh’s advice.
Source:IT








 Finance
Finance