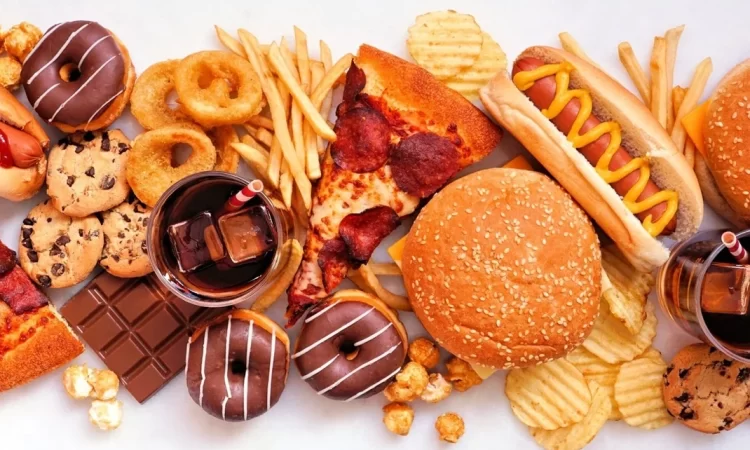
Over time, there has been an increase in the consumption of highly processed foods. The appealing marketing, convenient availability of these items, and hectic schedules that prompt individuals to go for these quick food options could all be contributors in this increased intake. Ultra-processed meals have been linked to a number of negative health outcomes, including high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, cardiac issues, and even cognitive decline. Instant noodles and soups, packaged breads, processed cheese products, breakfast cereals, crackers and chips, candy and ice cream, frozen or ready meals, baked goods (such as pizza, cakes, and pastries), reconstituted meats (such as sausages, nuggets, and fish fingers), processed ham, sodas, and other sweetened beverages are a few examples of ultra-processed foods. According to Dt Sonal Sureka, Nutritionist and Consultant on Practo, some of the risks associated with ultra-processed foods are as follows:
- Processed foods tend to contain added sugar and have a high amount of refined carbohydrate content; excess sugar can lead to compulsive overeating. This is associated with obesity, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes and other inflammatory diseases.
- Presence of artificial chemicals, which are added to increase the palatability and shelf life. These chemicals, like artificial colours, preservatives, texturing agents, etc., can affect the nutritional quality of the food. Intake of such foods also has an impact on your gut health and can lead to indigestion issues.
- Ultra-processed foods are very low in essential nutrients compared with whole or minimally processed foods. In some cases, manufacturers add synthetic vitamins and minerals to replace nutrients lost during processing. However, whole foods provide additional healthful compounds that ultra-processed foods do not.
- Ultra-processed foods often contain low-quality fat components. For example, they often contain refined seed or vegetable oils, which can be easy to use, inexpensive, and last a long time. These foods can add a substantial amount of trans fat to your body, which increases inflammation in the body and is associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes.
Source: InTv








 Finance
Finance